|
Understanding the Challenges of Spare Parts Business Today’s spare parts businesses face increasing complexity and competition. OEMs deal with low volume and high part variants. The growing list of variants leads to massive warehousing, a large inventory of obsolete parts. Additionally, intricate logistical efforts are needed, because products must be distributed and transported over long distances with high requirements, in terms of delivery and date reliability. It is becoming critical for companies to focus on supply chain integration, including internal constituents (allied functions) and external trading partners (contract manufacturers, suppliers, transportation carriers, and logistics providers). When compared with preceding industrial revolutions, the Industry 4.0 is unfolding at an exponential pace. One of the key risks of the modern supply chain is handling disruptions where technological, social, environmental, economic, and general market trends converge. However, many aftermarket supply chains are neither equipped nor orchestrated to cope effectively with the challenges. To conquer these fundamental challenges, OEMs are adopting Additive Manufacturing (AM) in actual production across different industry verticals. Additive Manufacturing – The Future Additive manufacturing (AM) is a unified term for a range of digital manufacturing technologies and processes, which build a component based on adding material, layer by layer, and binding powders, resins, metals or fluids into a component. As opposed to subtractive manufacturing methodologies, such as traditional machining, specific advantages of AM, compared to conventional manufacturing technologies, include:
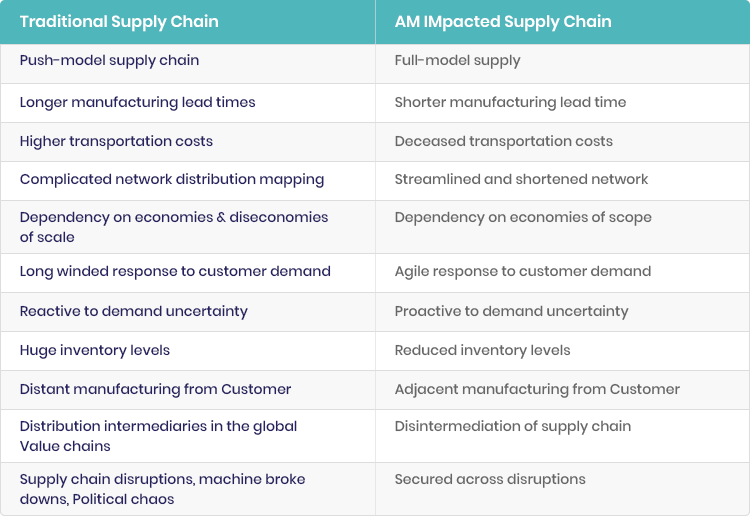
By extension, AM has the potential to impact global logistics and has implications for supply chain management. Due to these characteristics, AM has been labeled as ‘disruptive,’ due to its potential to affect the global economy, by changing the way products are designed and manufactured. Production of spare parts has been appointed as a highly interesting area for AM, as the technology presents opportunities for substantial gains, due to the spare parts supply chain significance and complexity. Traditional Supply Chain vs Additive Manufacturing Supply Chain AM has the potential to become the biggest single disruptive phenomenon to impact the industry globally since mass production lines were introduced in the early twentieth century. The technology has the potential to eliminate the need for high volume production facilities and low-level assembly workers, drastically reducing supply chain costs. AM does not need high level production facilities, since it can take place almost anywhere at the same cost. Therefore, it may no longer be financially efficient to transport products across the globe to get to the customer. With the potential to support re-shoring and local sourcing, the technology has the potential to tear established global supply chain structures apart and re-assemble it as a new, local system. Furthermore, AM streamlines the close relationship between design, manufacturing and marketing. By manufacturing items closer to their end destination, there is a greater potential to reduce logistics costs and environmental impact. As a result, the use of AM influences the potential for moving manufacturing activities away from low-cost countries and closer to the consumers. This technology could also transform a global supply chain and drive local supply chain integration. |
 |
|
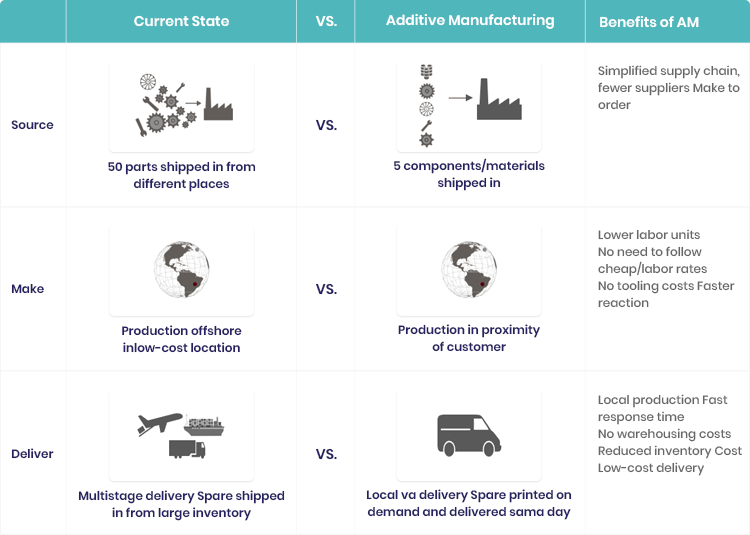
Shrinking the Supply Chain – AM impact |
 |
|
The race is on to use AM to produce spare parts on demand, and on location. To succeed in this journey, a detailed road map and dedicated execution team is required. At CGN Global, we collaborate with OEMs to transform and capitalize on the AM opportunities and help our clients embrace new opportunities, by creating scenarios and future-proofing supply chains for AM disruptions in using the CGN framework, as shown below. |
 |
© 2020 CGN. All rights reserved.